What Is A Cylinder Magnet Used For?
Overview
Cylinder magnets, characterized by their cylindrical shape and powerful magnetic fields, are a cornerstone of modern technology and everyday applications. These permanent magnets, typically made from materials like neodymium, ferrite, or alnico, generate a strong magnetic field along their axis, making them versatile for both industrial and consumer uses. Their compact, robust design allows them to deliver consistent magnetic performance in environments ranging from household gadgets to sophisticated scientific equipment. As magnets play a pivotal role in driving innovation, cylinder magnets stand out for their adaptability and strength.
The significance of magnets extends far beyond simple refrigerator decorations. They are integral to advancements in electronics, healthcare, energy, and scientific research. Cylinder magnets, in particular, are valued for their ability to fit into cylindrical components, deliver high magnetic strength, and maintain performance in challenging conditions. This blog post aims to explore the diverse applications of cylinder magnets, highlighting their properties, advantages, and challenges. By understanding their uses, we can appreciate how these unassuming components power cutting-edge technologies and enhance daily life.
At Heeger Magnet, we specialize in high-quality cylinder magnets with various specifications, ensuring optimal performance for industrial and scientific applications.
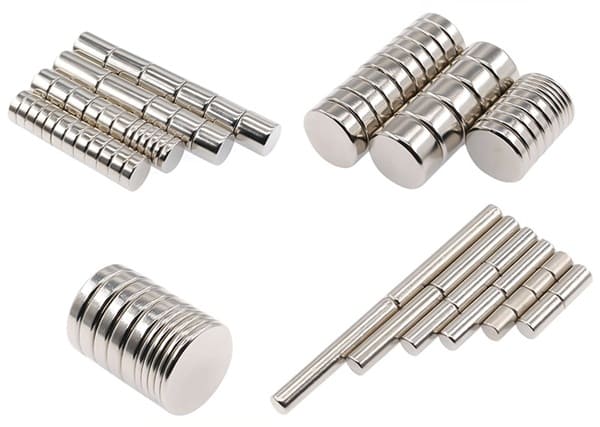

The Key Properties of Cylinder Magnets
Cylinder magnets are defined by their cylindrical shape, with a circular cross-section and a length that can vary from short discs to elongated rods. They are typically made from neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) for high strength, ferrite for cost-effectiveness, or alnico for temperature stability. Neodymium cylinder magnets, in particular, are prized for their exceptional magnetic strength, often exceeding 1 Tesla, making them among the strongest permanent magnets available. This strength is due to their high magnetic coercivity and remanence, which ensure a robust and stable magnetic field.
The magnetic field of a cylinder magnet is typically axially magnetized, meaning the north and south poles are located at the flat circular ends. This configuration produces a concentrated magnetic field along the magnet’s axis, ideal for applications requiring precise magnetic alignment, such as in motors or sensors. Physically, cylinder magnets vary in size (from millimeters to centimeters) and strength, with coatings like nickel or epoxy to enhance durability and resist corrosion. Their versatility in size and material allows them to be tailored for specific applications, from delicate electronics to heavy-duty industrial machinery.
1. Magnetic Properties
| Property | Description | Typical Values |
| Material | Common types: NdFeB (strongest), SmCo, AlNiCo, Ferrite | – NdFeB: Br up to 1.4 T – Ferrite: Br ~0.2-0.4 T |
| Magnetization Direction | Axially magnetized (N-S poles on flat ends) or radially magnetized | Measured at the pole surface |
| Surface Field (Gauss) | Measured at pole surface | – NdFeB: 3000-6000 G – Ferrite: 1000-2000 G |
| Coercivity (Hc) | Resistance to demagnetization | – NdFeB: 10-12 kOe – SmCo: 15-25 kOe |
| Energy Product (BH)max | Magnetic energy density | – NdFeB: 30-55 MGOe – Ferrite: 3-5 MGOe |
2. Physical/Dimensional Properties
| Property | Description | Examples |
| Standard Sizes | Diameter (D) × Height (H) ratios | Common: D3×H5mm, D10×H20mm, etc. |
| Tolerance | Dimensional accuracy | ±0.1mm (precision grade), ±0.5mm (standard) |
| Surface Finish | Coating/plating options | Ni-Cu-Ni (NdFeB), Epoxy (corrosion protection) |
| Weight | Calculated by density × volume | NdFeB: ~7.5 g/cm³ → D10×H20mm ≈ 11.8g |
3. Mechanical & Thermal Properties
| Property | Description | Values by Material |
| Tensile Strength | Resistance to breaking under tension | NdFeB: ~80 MPa (brittle) |
| Compressive Strength | Withstands crushing forces | NdFeB: ~1100 MPa |
| Max Operating Temp | Temperature limit before demagnetization | – NdFeB: 80-200°C (grades N to EH) – SmCo: 250-350°C – Ferrite: 250°C |
| Thermal Expansion | Dimensional change with temperature | NdFeB: ~5-7 ×10⁻⁶/°C (parallel to magnetization) |
4. Environmental Resistance
| Property | Description | Comparison |
| Corrosion Resistance | Vulnerability to oxidation/rust | – NdFeB: Poor (requires coating) – SmCo/Ferrite: Good |
| Humidity Resistance | Performance in wet conditions | Ni-plated NdFeB: Excellent |
| Radiation Resistance | Stability in high-radiation environments | SmCo: Best (used in aerospace) |
5. Electrical & Other Properties
| Property | Description | Notes |
| Conductivity | Electrical resistivity | NdFeB: ~1.4 μΩ·m (semi-conductive) |
| Curie Temperature | Temp where magnetism is lost | – NdFeB: 310-400°C – Ferrite: 450°C |
| Machinability | Ease of drilling/cutting | – All sintered magnets are brittle. – Diamond tools are required. |
6. Comparison of Material Types
| Property | Neodymium (NdFeB) | Ferrite (Ceramic) | AlNiCo | Samarium Cobalt (SmCo) |
| Composition | Nd₂Fe₁₄B | SrO·6Fe₂O₃ or BaO·6Fe₂O₃ | Al-Ni-Co-Fe alloy | Sm(Co,Fe,Cu,Zr)₇-8 |
| Grade Examples | N35-N52, 33M-50M | C1-C10 | AlNiCo 5, AlNiCo 8 | SmCo5, Sm₂Co₁₇ |
| Remanence (Br) | 1.0-1.4 T | 0.2-0.4 T | 0.6-1.4 T | 0.8-1.1 T |
| Coercivity (Hc) | 800-2000 kA/m | 120-320 kA/m | 50-150 kA/m | 600-2000 kA/m |
| Intrinsic Coercivity (Hci) | 800-3000 kA/m | 200-400 kA/m | 50-150 kA/m | 600-3000 kA/m |
| Energy Product (BH)max | 30-55 MGOe | 3-5 MGOe | 5-10 MGOe | 18-32 MGOe |
| Curie Temperature (Tc) | 310-400°C | 450°C | 700-860°C | 700-850°C |
| Max Operating Temp | 80-200°C (grade dependent) | 250°C | 550°C | 250-350°C |
| Temp Coefficient (αBr) | -0.12%/°C | -0.2%/°C | -0.02%/°C | -0.04%/°C |
| Density | 7.3-7.5 g/cm³ | 4.8-5.1 g/cm³ | 7.0-7.3 g/cm³ | 8.2-8.5 g/cm³ |
| Vickers Hardness | 500-600 HV | 500-600 HV | 500-600 HV | 400-500 HV |
| Tensile Strength | 80 MPa | 50 MPa | 150 MPa | 70 MPa |
| Compressive Strength | 1100 MPa | 400 MPa | 600 MPa | 900 MPa |
| Electrical Resistivity | 1.4 μΩ·m | 10⁴-10⁶ μΩ·m | 0.5 μΩ·m | 0.8 μΩ·m |
| Corrosion Resistance | Poor (requires coating) | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Machinability | Brittle (diamond tools) | Brittle | Machinable | Brittle |
Looking for top-quality cylinder magnets? Explore Heeger Magnet’s selection.
Common Applications of Cylinder Magnets
Cylinder magnets are employed in a wide array of applications due to their strong magnetic fields and versatile shape. In industrial settings, they are critical components in magnetic separators, which remove ferrous contaminants from materials in industries like mining, recycling, and food processing. They are also integral to electric motors and generators, where their axial magnetic fields drive rotational motion, powering everything from industrial machinery to electric vehicles. The precise field alignment of cylinder magnets ensures efficient energy conversion in these systems.
In consumer electronics, cylinder magnets are found in speakers and headphones, where they interact with voice coils to produce sound through magnetic vibrations. They are also used in hard disk drives, enabling precise data reading and writing by positioning read/write heads. In medical applications, cylinder magnets contribute to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, generating strong fields for imaging, and are used in magnetic therapy devices to alleviate pain. In scientific research, they play a role in particle accelerators, guiding charged particles, and in magnetic levitation experiments, enabling frictionless motion.
1. Electronics & Consumer Devices
| Application | Magnet Type | Why Cylinder Magnets? | Example Products |
| Speakers/Headphones | Ferrite, NdFeB | Axial field for diaphragm vibration | Earphones, tweeters |
| Sensors | NdFeB, SmCo | Precise axial field detection | Hall effect sensors, reed switches |
| Relays & Switches | NdFeB | Strong pull force in compact size | Automotive relays |
2. Industrial & Manufacturing
| Application | Magnet Type | Why Cylinder Magnets? | Example Uses |
| Magnetic Holders | NdFeB | High holding force per unit volume | Jig fixtures, tooling |
| Separators | Ferrite | Cost-effective for bulk material sorting | Food processing, recycling |
| Couplings | SmCo | Torque transmission without contact | Pump systems, cleanrooms |
3. Automotive & Aerospace
| Application | Magnet Type | Why Cylinder Magnets? | Implementation |
| Stepper Motors | NdFeB | High energy density for precision control | Fuel injectors, HVAC flaps |
| Speed Sensors | SmCo | Temperature-resistant signal generation | Wheel speed sensors |
| Actuators | AlNiCo | Reliable performance under hood temps | Transmission systems |
4. Medical & Scientific
| Application | Magnet Type | Why Cylinder Magnets? | Devices |
| MRI Components | NdFeB (Ni-plated) | Ultra-strong field uniformity | Gradient coils |
| Lab Equipment | SmCo | Corrosion-resistant precision | Mass spectrometers |
| Surgical Tools | Sterilized NdFeB | Compact size for internal guidance | Laparoscopic devices |
5. Renewable Energy
| Application | Magnet Type | Why Cylinder Magnets? | Systems |
| Wind Turbine Generators | NdFeB (high-temp grade) | High torque-to-weight ratio | Direct-drive systems |
| Hydrogen Fuel Cells | SmCo | Stability in corrosive environments | PEM fuel cells |
Explore our optimized cylinder magnets.
Key Benefits of Cylinder Magnets
Cylinder magnets offer distinct advantages that make them ideal for specific applications. Their high magnetic strength, particularly in neodymium variants, allows for compact designs without sacrificing performance. In electric motors, for example, a small cylinder magnet can generate the torque needed for powerful machinery, reducing size and weight compared to other magnet shapes. This compactness is critical in applications like drones or portable electronics, where space is at a premium.
The cylindrical shape is inherently versatile, fitting seamlessly into components like rotors, sensors, or magnetic couplings, where circular geometry is common. This adaptability ensures precise integration into complex systems, enhancing efficiency. Additionally, ferrite cylinder magnets are cost-effective for large-scale industrial applications, such as magnetic separators, where high strength is less critical than affordability. The combination of strength, shape, and cost-effectiveness makes cylinder magnets a preferred choice across industries.
Here are their core benefits:
1. Predictable Magnetic Field Orientation
- Axial Magnetization: Poles are consistently aligned at the flat circular ends, creating a straight, uniform field along the axis.
- Radial Options Available: For specialized applications requiring a 90° field shift (e.g., rotary encoders).
2. Optimal Strength-to-Size Ratio
- Concentrated Flux Density: The cylindrical shape focuses magnetic energy at the poles, generating strong pull forces despite small sizes. (Data: A Ø10mm × 10mm N52 NdFeB magnet can lift over 12 kg vertically.)
- Efficient Material Use: No wasted material compared to complex shapes (e.g., arcs or rings).
3. Mechanical Versatility
- Easy Integration: Simple cylindrical form fits seamlessly into bores, housings, and shafts. (Applications: Motor rotors, bearing assemblies, and tooling fixtures.)
- Durable Coatings: Nickel, epoxy, or gold plating protect against chipping/corrosion (critical for NdFeB).
4. Thermal & Environmental Adaptability
| Material | Max Temp | Corrosion Resistance | Best Use Case |
| NdFeB | 80–200°C | Poor (needs coating) | High-strength indoor apps |
| SmCo | 250–350°C | Good | Aerospace/automotive |
| Ferrite | 250°C | Excellent | Outdoor/low-cost |
| AlNiCo | 550°C | Good | High-temp sensors |
5. Cost-Effective Customization
- Wide Size Range: Diameters from 1 mm to 50+ mm with customizable height-to-diameter ratios. (Example: Tiny Ø1mm × 1mm magnets for micro-mechanical devices vs. Ø50mm × 100mm for industrial separators.)
- Affordable Ferrite Option: Lowest cost per unit volume for non-critical applications (e.g., fridge seals).
6. Dynamic Performance in Motion Systems
- Balanced Rotation: Symmetrical shape minimizes vibration in motors and generators.
- Low Eddy Current Losses: Solid cylinders (vs. segmented designs) simplify high-speed rotor assemblies.
7. Safety & Handling Benefits
- Rounded Edges: Safer to handle than block magnets with sharp corners.
- No Sharp Flux Gradients: Reduces the risk of sudden snapping (unlike thin discs or rings).
At Heeger Magnet, we supply premium-grade cylinder magnets that meet international IEC, ISO, and ASTM standards, guaranteeing exceptional magnetic performance and reliability.
Cylinder magnets excel where directional field control, space efficiency, and ease of integration are critical. Their versatility spans from micro-electronics to heavy industrial systems.
Despite their versatility, cylinder magnets face challenges that must be considered. Neodymium magnets, while powerful, are susceptible to demagnetization at high temperatures (above 80–200°C, depending on the grade), limiting their use in applications like high-temperature engines. Ferrite magnets, though more temperature-resistant, have lower magnetic strength, which may not suffice for high-performance applications. Additionally, neodymium magnets are brittle and prone to cracking under mechanical stress, requiring careful handling.
Safety is a significant concern due to the strong magnetic fields of cylinder magnets, particularly neodymium ones. These fields can attract metal objects unexpectedly, posing risks of injury or damage to equipment. Environmental considerations also arise, as neodymium magnets rely on rare earth elements, whose extraction is resource-intensive and environmentally damaging. Recycling and sustainable sourcing are critical to mitigating these impacts. Proper design and handling protocols are essential to maximize the benefits of cylinder magnets while addressing these challenges.
Request a custom quote for high-quality cylinder magnets.
FAQ
| Question | Answer |
| What are cylinder magnets used for? | Cylinder magnets are used in motors, sensors, MRI machines, magnetic separation, and electronics. |
| Why are cylinder magnets preferred in motors? | Cylinder magnets provide a uniform magnetic field, making them ideal for efficient motors. |
| Can cylinder magnets be used in consumer electronics? | Yes, they are used in devices like speakers, microphones, and electric toothbrushes. |
| How strong are cylinder magnets? | Cylinder magnets, especially neodymium ones, are very strong and provide high magnetic strength. |
| Are cylinder magnets used in medical applications? | Yes, they are used in MRI machines to generate strong, stable magnetic fields for imaging. |
| How long do cylinder magnets last? | Cylinder magnets, especially those made of neodymium or samarium-cobalt, are highly durable. |
Cylinder magnets are indispensable components in modern technology, powering applications from industrial machinery to medical imaging and scientific research. Their high magnetic strength, versatile shape, and adaptability make them ideal for diverse uses, including motors, speakers, MRI machines, and magnetic levitation systems. Despite challenges like demagnetization, brittleness, and environmental concerns, their benefits far outweigh the drawbacks, driving innovation across industries.
As technology advances, cylinder magnets will continue to play a critical role in developing efficient, compact, and sustainable solutions. Ongoing research into improving magnet materials, recycling methods, and safety protocols will further enhance their impact.
For top-quality cylinder magnets, Heeger Magnets provides tailored solutions for various applications.
Looking for premium cylinder magnets? Contact us today!
 Call us now: 925-385-8104
Call us now: 925-385-8104